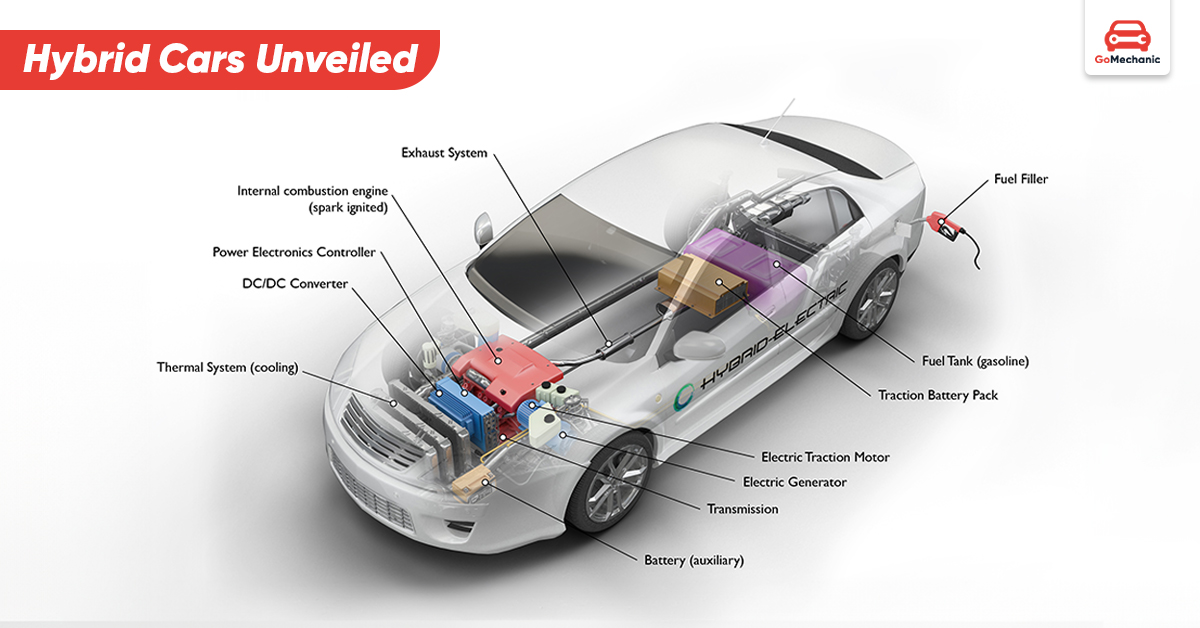
Hybrid cars utilize a conventional Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) along with an electric motor system. This combination may result in higher efficiency, regarding fuel consumption and reduced emissions. It also increases the engine’s lifespan.
Main Components
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): ICE is the traditional petrol or diesel powered engine usually used to power cars.
- Electric Motor: An electric motor can either work in isolation or together with the ICE to provide power to move the vehicle.
- Battery: Electrical energy is stored in the battery to feed the electric motor when needed.
- Powertrain Control Unit (PCU): This computer controls the interplay between the ICE and the electric motor for better performance and fuel efficiency.
How it Works
The car always starts in electric mode. The battery powers the electric motor driving the wheels. The electric motor is capable of providing sufficient power during low speed driving or cruise conditions where the engagement of the ICE is not required. During higher loads, the ICE can assist or take over to give further torque and speed. As the car decelerates, the electric motor can act like a generator to capture kinetic energy. Then it channels it into the battery. The battery becomes recharged, and the wear on the brakes is decreased as well.
Types of Hybrids

Parallel Hybrid
The parallel hybrid car consists of an electric motor coupled with a conventional ICE. Both facilitate power to the wheels. The power into the wheel can be driven by either an ICE or an electric motor alone, or together.
Series hybrid
In a series hybrid car, the ICE generates electricity to actuate an electric motor. The car wheels are powered by the electric motor only. It does not use a combination of both the ICE and the electric motor.
Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicle (PHEV)
In simple terms, any conventional hybrid car with a battery that can be charged using an external power source is a PHEV. The PHEV allows for longer “electric only” driving ranges as compared to any other type of hybrid.
Range-Extended Electric Vehicle (REEV)
Another form of plug-in hybrid is the REEV, where most of the drivetrain takes the form of an electric motor driving the wheels. The ICE acts purely as a generator to recharge the battery when the “electric only” range is depleted.
How does Hybrid technology differ from ICE and Electric Vehicles?
Hybrid Technology
Hybrids use both an ICE and an electric motor. Power can be drawn from either of them or both. The electric motor assists the ICE during acceleration. And regenerative braking captures energy, thereby allowing for superior fuel economy. The electric motor lowers emissions, especially in cities. The hybrids are available in a number of formatslike parallel, series, plug-in, and range-extended and all offer different levels of capabilities.
Internal Combustion Engine
Vehicles using this engine are solely powered by petrol or diesel. They normally emit more smoke compared to hybrid or pure EVs. But often have a lower initial purchase price than pure EVs or Hybrids. An ICE is basically a type of heat engine that internally converts chemical energy into mechanical work. This is achieved by the combustion of a certain fuel. The fuel burns inside the combustion chamber. The hot gasses that result from this combustion act on a piston, which, in turn, produces a rotary motion.
Electric Vehicles
The EVs run on batteries powering an electric motor, giving zero tailpipe emissions. They go further on a single charge than the hybrids. The operating cost, besides, is generally less expensive since electricity is cheaper compared to petrol. Compared to hybrids or conventional ICE vehicles, the purchase cost is normally higher for EVs.
Reasons to Choose Hybrid Vehicles

Hybrid cars emit significantly less smoke than the typical petrol powered ones. Hybrids promote cleaner air and a healthier environment. Most of the time, they also provide better fuel economy compared to the traditional vehicle. It cuts down on your carbon footprint and saves you some money on fuel costs. In addition, they use less fuel, translating into remarkable savings on fuel over time. Many places also give people tax credits or incentives when driving a hybrid car, saving them money. Hybrids tend to retain a better resale value at times of resale or trade-in.
Conclusion
Hybrid cars are one of the biggest leaps into the future. They bring together efficiency and smoothness from an electric motor with the flexibility of an ICE. Considering the different kinds of hybrids and their unique advantages will let you know if a hybrid car fits your needs or style of driving.
Hybrids present an outstanding combination of environmental benefits, economic advantages, and features of performance enhancement. Starting with reduced emissions and fuel efficiency, to acceleration and quieter run time, hybrid cars surely present a more pleasurable and environment-friendly driving experience. And as hybrids keep on getting better, more innovative, and more efficient, it is expected that the coming years will bring even more excitement.